Cardiovascular Health: Your Guide to a Stronger Heart

Cardiovascular health is an essential component of overall wellness, significantly impacting how we feel and function daily. With cardiovascular diseases (CVDs) being one of the leading causes of death worldwide, understanding the factors that contribute to a healthy heart is vital for everyone. In this guide, well delve into the core aspects of cardiovascular health, including its definition, importance, risk factors, and proactive measures you can take to maintain your hearts health.
What is Cardiovascular Health?
Definition of Cardiovascular Health
Cardiovascular health refers to the well-being of your heart and blood vessels, encompassing how effectively they function in circulating blood throughout the body. This system plays a crucial role in delivering oxygen and nutrients to various organs and tissues, while also removing waste products. A healthy cardiovascular system can help prevent diseases, maintain energy levels, and promote a long, active life.
Importance of Cardiovascular Health
Maintaining good cardiovascular health is critical for several reasons:
- Prevention of Diseases: Cardiovascular diseases, including heart attacks and strokes, can result from poor heart health. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), these diseases are responsible for 31% of all global deaths.
- Improved Quality of Life: A healthy cardiovascular system ensures that your body receives the necessary oxygen and nutrients, leading to increased energy and overall well-being.
- Enhanced Longevity: Individuals with better cardiovascular health often experience longer lifespans and reduced risk of chronic illnesses.
Major Components of Cardiovascular Health
Heart Anatomy and Function
To appreciate the importance of cardiovascular health, its essential to understand the anatomy of the heart. The heart is a muscular organ composed of four chambers: two atria and two ventricles. It functions as a pump, circulating blood through two primary circuits:
- Pulmonary Circuit: Transports deoxygenated blood from the heart to the lungs for oxygenation.
- Systemic Circuit: Carries oxygen-rich blood from the heart to the rest of the body.
Blood Vessels and Circulation
The blood vessels play a crucial role in cardiovascular health, transporting blood to and from the heart. They include:
- Arteries: Carry oxygen-rich blood away from the heart to the body.
- Veins: Return deoxygenated blood back to the heart.
- Capillaries: Microscopic vessels where the exchange of oxygen, nutrients, and waste occurs.
Understanding how these components work together can help emphasize the importance of maintaining cardiovascular health.
Key Functions of the Cardiovascular System
The cardiovascular system serves several essential functions:
- Nutrient Transport: Delivers nutrients from digested food to cells.
- Waste Removal: Transports waste products to organs for excretion.
- Temperature Regulation: Helps maintain body temperature by redistributing blood flow.
- Hormonal Distribution: Transports hormones to various organs, regulating numerous bodily functions.
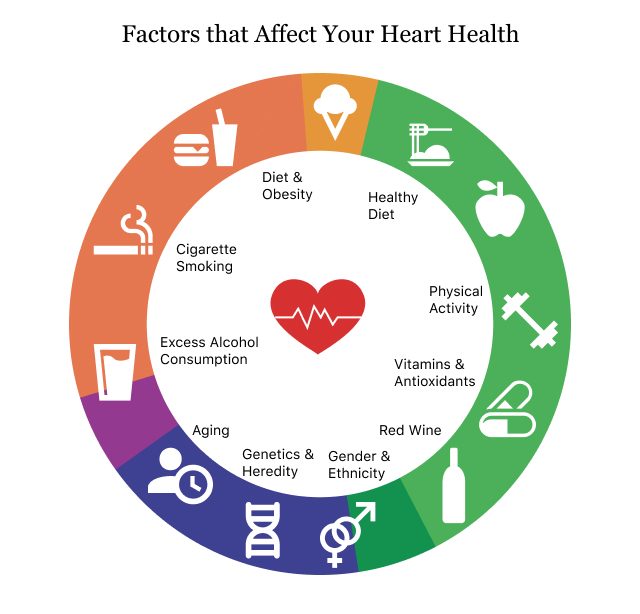
Risk Factors Affecting Cardiovascular Health
Understanding the risk factors associated with cardiovascular health is essential for prevention. They can be classified into two categories: modifiable and unmodifiable.
Unmodifiable Risk Factors
These are factors that cannot be changed but can influence your heart health:
- Age: Risk increases as you grow older.
- Genetics: Family history of heart disease can elevate your risk.
Modifiable Risk Factors
These factors can be controlled through lifestyle changes:
- High Blood Pressure: Also known as hypertension, it significantly increases the risk of heart disease.
- High Cholesterol: Elevated levels of LDL cholesterol can lead to plaque buildup in arteries.
- Obesity: Excess weight can strain the heart and increase the risk of heart disease.
- Sedentary Lifestyle: Lack of physical activity contributes to several heart disease risk factors.
The Role of Genetics in Cardiovascular Health
While you cannot change your genetic predisposition, being aware of your family’s health history can guide your decisions regarding lifestyle changes and preventive care.
Signs and Symptoms of Cardiovascular Issues
Recognizing the signs and symptoms of cardiovascular problems can save lives. Early detection is key.
Common Cardiovascular Diseases
Several diseases fall under the umbrella of cardiovascular health, including:
- Coronary Artery Disease: A condition where plaque builds up in the arteries, leading to reduced blood flow to the heart.
- Heart Failure: A chronic condition where the heart cannot pump blood effectively.
- Arrhythmias: Irregular heartbeats that can lead to serious complications.
Early Warning Signs to Watch For
Being aware of early warning signs can facilitate timely medical intervention. Common symptoms include:
- Chest pain or discomfort
- Shortness of breath
- Dizziness or lightheadedness
- Palpitations or irregular heartbeat
If you experience any of these symptoms, it’s crucial to seek medical attention promptly.
Stay tuned for the second half of this article, where we will explore effective strategies to maintain your cardiovascular health, the role of diet and exercise, and when to consult a healthcare professional.
Strategies for Maintaining Cardiovascular Health
Maintaining cardiovascular health requires a proactive approach that encompasses lifestyle changes, dietary modifications, and regular check-ups. Here, well explore effective strategies you can adopt to keep your heart healthy and reduce your risk of cardiovascular diseases.
1. Healthy Eating Habits
The food you consume plays a significant role in your heart health. Incorporating the following dietary practices can lead to a healthier cardiovascular system:
- Focus on Whole Foods: Prioritize fresh fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats. Foods rich in antioxidants, fiber, and omega-3 fatty acids, such as salmon and walnuts, can support heart health.
-
Limit Processed Foods: Reduce your intake of high-sugar and high-sodium processed foods. These can increase blood pressure and contribute to weight gain.
-
Monitor Cholesterol Levels: Include foods that help lower cholesterol, such as oats, beans, and fatty fish. Additionally, limit saturated fats found in red meats and full-fat dairy products.

2. Regular Physical Activity
Engaging in regular exercise is crucial for maintaining cardiovascular health. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate aerobic activity each week, such as walking, cycling, or swimming. Here are some tips to incorporate exercise into your routine:
- Find Activities You Enjoy: Exercise doesn’t have to be a chore. Dancing, hiking, or playing sports can make working out more enjoyable.
-
Strength Training: Incorporate strength training exercises at least twice a week to improve muscle strength and overall health.
-
Stay Consistent: Set realistic goals and gradually increase your activity level to ensure consistency over time.
3. Stress Management
Chronic stress can have detrimental effects on heart health, leading to increased blood pressure and unhealthy coping mechanisms. Here are some effective strategies to manage stress:
- Mindfulness and Meditation: Practices such as yoga and meditation can help reduce stress and promote relaxation. Consider dedicating a few minutes each day to mindfulness exercises.
-
Adequate Sleep: Prioritize getting enough quality sleep, as poor sleep patterns can negatively affect heart health. Aim for 7-9 hours of sleep each night.
-
Connect with Others: Maintain a strong support network of friends and family. Engaging in social activities can provide emotional support and help alleviate stress.
4. Regular Health Screenings
Regular check-ups are essential for monitoring your cardiovascular health. Work with your healthcare provider to schedule the following assessments:
- Blood Pressure Checks: Aim for a blood pressure reading below 120/80 mm Hg to reduce your risk of heart disease.
-
Cholesterol Levels: Get your cholesterol levels checked regularly, and discuss with your doctor how to manage them effectively.
-
Diabetes Screening: Diabetes is a significant risk factor for heart disease, so regular screening is crucial, especially if you have a family history.
5. Avoid Tobacco and Limit Alcohol
-
Quit Smoking: Smoking is a major risk factor for cardiovascular disease. Quitting can significantly improve your heart health and overall well-being.
-
Limit Alcohol Consumption: If you drink alcohol, do so in moderation. This means up to one drink per day for women and up to two drinks per day for men.
FAQs About Cardiovascular Health
Q1: What are the best foods for cardiovascular health?
A1: Foods such as fatty fish, whole grains, fruits, vegetables, nuts, and seeds are excellent for heart health.
Q2: How can I reduce my risk of heart disease?
A2: By maintaining a healthy diet, engaging in regular physical activity, managing stress, avoiding tobacco, and scheduling regular health screenings.
Q3: What symptoms should I be aware of?
A3: Chest pain, shortness of breath, dizziness, and irregular heartbeats are signs that warrant medical attention.
Conclusion
Taking charge of your cardiovascular health is essential for leading a long, healthy life. By adopting healthier eating habits, staying physically active, managing stress, and keeping up with regular health screenings, you can significantly reduce your risk of cardiovascular diseases.
Additional Resources
For more information on cardiovascular health, consider checking out the following resources:
Remember, small changes can lead to significant improvements in your heart health over time. Take the first step today for a healthier tomorrow!

